- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-21 Origin: Site








You can use aseptic equipment such as Raw Material Preparation Equipment, Juice Extraction and Blending Equipment, Sterilization Systems, Sterile Filtration Systems, Aseptic Blending Tanks, Aseptic Filling Machines, Capping and Sealing Equipment, Secondary Packaging Equipment, etc. to ensure the safety of beverages during aseptic processing. These tools help stop contamination and protect beverages products. When you use advanced aseptic processing, you lower the chance of contamination from workers. This kind of contamination has stopped manufacturing in real cases. The Most Probable Number technique helps you check that your aseptic filling machine and other systems keep the product free from germs. In sterile product manufacturing, picking the right equipment helps you follow rules and make sure you always have high-quality aseptic production.
Aseptic equipment such as capping, sealing , and filling machines keep products safe from germs. These tools help make sure products stay clean during processing. Picking the right equipment makes products better and lowers the chance of germs getting in. It also helps companies follow safety rules. Cleanrooms and sterilization methods work together to keep the area clean. They protect products from germs. Advanced aseptic filling machines limit human touch. They save energy and make products faster. These machines also keep products free from germs. Regular testing, training, and maintenance are very important. They help make sure aseptic equipment works well and meets safety rules.

You help keep products safe in aseptic processing. Sterility assurance means you use strict rules to stop germs. You follow special steps for making and testing products. You check each batch for germs using sampling plans. These checks help you know your products are safe. You use risk-based ways to fix problems if they happen. You train your team and design your building to stay clean. You watch the environment to keep it safe. You check the sterility assurance level, often aiming for a SAL of 10^-6 or better. This means less than one non-sterile unit in a million. You review and update your safety steps often to keep them strong.
Process validation protocols show you what to do.
Sampling plans help you look for germs and particles.
You use risk management to make control plans.
You train workers and watch the environment.
You test for sterility with methods like membrane filtration.
You need cleanrooms for aseptic processing. Cleanrooms use HEPA filters, air showers, and special clothes to keep out dust and germs. These steps lower the risk of germs and particles. You control temperature, humidity, and air to keep things steady. This helps you get the same results every time. Cleanrooms can be changed for different needs. Studies show people cause almost half of all particle problems in cleanrooms. You lower this by using protective gear and washing hands well.
HEPA filters and air showers take out particles.
Gowning keeps germs away.
You watch air, temperature, and humidity.
You teach staff to use aseptic techniques.
You use different sterilization methods in aseptic processing. Autoclaving is very strong. It uses high heat and pressure to kill all germs. Chemical methods like chlorhexidine and glutaraldehyde work too, but not as well. You often use aseptic processing with terminal sterilization for sensitive products. This mix helps you reach a high sterility assurance level. You check each sterilization step with germ tests and real-time data. You also check your equipment and steps to make sure they work.
| Sterilization Method | Sterility Efficacy (%) | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Autoclaving (121°C, 15 min) | 100 | Kills all germs for many tools |
| Chlorhexidine (2%) | 87 | Some germs may stay |
| Glutaraldehyde | 60 | Not as strong, more risk of germs |
You pick the best sterilization method for your product and process.
You use aseptic equipment to keep products safe from germs. The main goal is to stop contamination at every step. You work in clean rooms and use machines that limit people touching products. This helps protect things like juices.
Aseptic processing has many steps to keep things sterile. First, you clean and sterilize all the equipment. Special filters and barriers block germs from getting in. Robots fill and seal containers without touching them. Artificial intelligence checks sensor data to find problems early. Single-use systems are easy because you throw away used parts. This means you do not need to clean them. Real-time monitoring lets you see if the area stays safe. If something goes wrong, you can fix it fast.
You follow strict rules and test your machines often. You check if they work well at different speeds and temperatures. You also make sure every part is safe to use. The table below shows some important details for aseptic processing equipment:
| Aspect | Description | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Qualification Models | Risk-based equipment checks | 4Q model (DQ, IQ, OQ, PQ); test at all limits |
| Validation Principles | Science-based, risk-focused | Focus on quality, design, and good practice |
| User Requirements | Full range and material checks | Defines how equipment should work and change |
| Qualification Testing | Multi-stage testing | Checks parts, sensors, and performance |
| Changeover Procedures | Steps for switching products | Clear rules for cleaning and setup |
| Product Assessments | Checks for material safety | Looks for leaks or changes in product |
| Parameter Verification | Tests for control | Runs at high and low settings |
| Regulatory Focus | Quality and risk control | Meets all safety and use rules |
Aseptic equipment is special because it keeps products safe and follows strict rules. Some machines use isolators to keep products away from people. This lowers the risk of germs. Isolators work better than RABS because they give full protection. Some equipment is made for heat-sensitive products, which is important in aseptic processing.
You use machines that watch air quality and germs all the time. This helps you act fast if something changes. Many systems use single-use parts, so you do not have to clean them or worry about mixing products. Some machines work with many types of containers and products.
Tip: Pick equipment that lowers human contact and meets the newest GMP standards. This helps you follow new rules and keeps your products safe.
Industry rules, like those from the European Pharmacopeia and United States Pharmacopeia, set high standards for sterility and equipment design. These rules push you to use advanced aseptic processing tools. This lowers contamination risks and helps you make safe, high-quality products.
Good raw material preparation keeps products clean and high quality. This equipment helps stop contamination early. Many systems use automation, so work is faster and more reliable. Quality control tools like Aerobic Plate Count and ATP bioluminescence help find germs or particles fast.
| Quality Control Metric | Role in Validating Equipment Performance |
|---|---|
| Aerobic Plate Count | Finds germs in the product |
| Yeast/Mold Tests | Checks for fungus |
| ATP Bioluminescence | Gives quick germ checks |
These systems need a lot of space and money. Maintenance is hard because there are many moving parts. Cleaning and sterilizing take time and effort, which can slow things down.
You get more juice and better results, especially with peeled fruit. The machines are easy to use and fix, so they work well every day. You can make different recipes and batch sizes as needed.
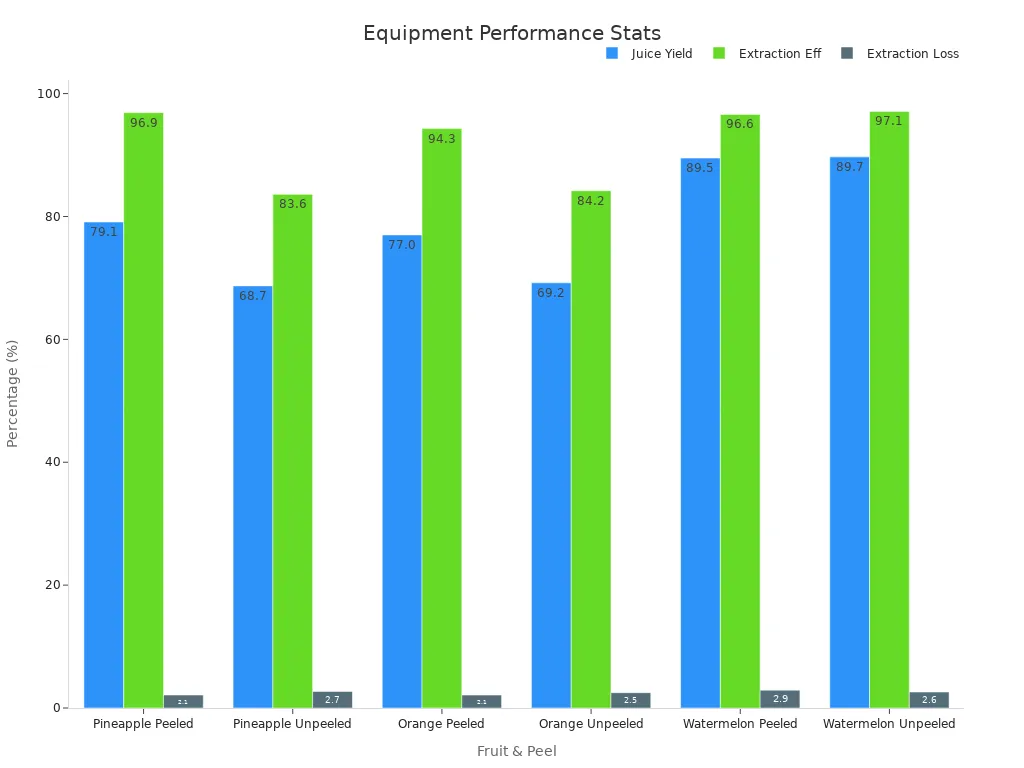
These machines use a lot of energy, especially in big factories. Some product can be lost when you switch batches. You need to watch for particles that can lower product quality.
Sterilization systems kill germs and keep products safe. Automated methods like Steam-in-Place save time and work. You get strong germ control, checked by biological indicators and Sterility Assurance Levels.
These systems need careful control and watching. They cost a lot at first. You must follow cleaning rules closely to avoid problems.
Sterile filtration adds another safety step against germs. It makes products clearer and last longer. Filters are easy to change, so work goes smoothly.
Filters need to be changed often. If you do not care for the system, some germs may stay. Changing filters can stop production for a while.
These tanks keep things sterile while mixing and storing. You can use them for batches or nonstop work. Cleaning and decontamination are automatic, so conditions stay safe.
Tanks need more floor space. They must be checked and fixed often. If they break, products can spoil or get dirty.
These machines keep products sterile while packaging. They work fast and automatically, so mistakes are fewer. You can use them for many container types and sizes. Robotic and aseptic designs lower the risk of particles and germs. Studies show advanced machines can reach zero germs and over 99% good results in tests.
These machines are complex and need skilled workers. If they stop, production slows down. They cost a lot at first, but help control germs in the long run.
These machines close products tightly and keep out germs. Induction sealing stops air, germs, and leaks, so products last longer. Tamper-evident seals make products safer and help buyers trust them.
These machines add to the total cost. They may need more space. You must keep them working well to make sure seals are good and no particles get in.
This equipment keeps products safe during shipping and storage. Packaging helps with branding and tracking. Automated systems make work faster and easier.
These machines need a lot of space and money. Cleaning and fixing them can be hard. Packaging materials also raise costs.
You need strong contamination control when picking aseptic filling equipment. Modern machines watch for particles all the time. They give alerts if too many particles show up. You can see limits for different particle sizes. This helps you act fast if there is a problem. Online particle counters check every step, from filling to capping. These systems lower contamination risk by keeping people away from key areas. You can use the Intervention Risk (IR) score. This score shows how often workers touch the process. Fewer touches mean less risk. You should also check important tests and standards:
| Selection Criterion | Description and Quantitative Data |
|---|---|
| Helium Leak Test | Finds seal leaks under real processing conditions. |
| Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) | Needs to be 10^-6 or better for effective sterilization. |
| Bacterial Endotoxin Limit | Must stay below 0.25 EU/mL to control endotoxin contamination. |
Using Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment helps you set up smart, science-based controls. This way, you lower contamination and keep your process safe.
You must follow strict rules in aseptic processing. Many companies update documents and risk checks to follow the rules. They compare their work to EU GMP Annex 1 and other guides. New aseptic tools help you meet these standards. You also need to train your team and keep records of every step. Corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) help you fix problems fast. Using advanced aseptic filling machines shows you care about safety and quality. This builds trust and keeps your products safe.
Note: Always try to get better and do regular checks to be ready for inspections.
For incoming raw materials, laboratory tests are used to strictly control various indicators: measuring particle size to ensure uniformity, detecting water content to assess stability, checking for impurities to ensure purity, and determining pH to monitor the acid-base environment. These detailed raw material data provide a scientific basis for the calibration of aseptic filling equipment and the setting of process parameters, enabling the equipment to adapt to specific raw material characteristics and start the production process. The table below shows how product data helps you choose equipment:
| Data Category | Description | Impact on Equipment Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming Raw Material Quality | Particle size, water content, impurities, pH | Sets calibration and process parameters |
| Final Product Quality | Microbial control, active ingredient, impurity levels | Confirms equipment can meet product standards |
You also test temperature, pressure, and humidity controls. These steps make sure your equipment works well for your products.
You want your aseptic process to run fast and smooth. You measure how long each step takes, from cleaning to sealing. You count how many trays or bottles are left at the start of each shift. You check if all parts are there and working. Fast delivery times show good planning. Customer surveys help you see if your process is good. You also keep your equipment checked and fixed, following ISO 14644 and USP <797>. Regular training and checks help your team do better. Using advanced aseptic filling equipment helps you work faster and keep products safe.
Picking the right aseptic equipment helps keep products safe. It also helps you follow rules and work well. Every kind of equipment has its own good and bad points. You should look at how easy it is to clean and what help you get after buying. Here is a checklist to help you:
Make sure the sterility assurance level is right
Think about how much care the equipment needs
Choose equipment that fits your product
Find out if you get help after buying
For better results, check out machines like the Jiangsu EQS. You can also ask suppliers or read the latest rules to get the best outcome.
Aseptic equipment protects products from bacteria and ensures that no harmful substances enter during processing. Aseptic equipment is required for the production of food and beverages. It helps to ensure the high quality and safety of products.
An aseptic filling machine uses special cleaning steps. These steps keep the area free from germs and dust. Cleanroom technology helps keep things extra clean. This makes sure products stay safe and sterile.
Sterilization kills all germs, even the tough ones. Decontamination lowers the number of germs but does not get rid of them all. Both are used to help keep products safe and clean.
Contamination control keeps products safe from germs and dust. You use special machines to lower the risk of problems. Good control means products are safe and high quality for people to use.